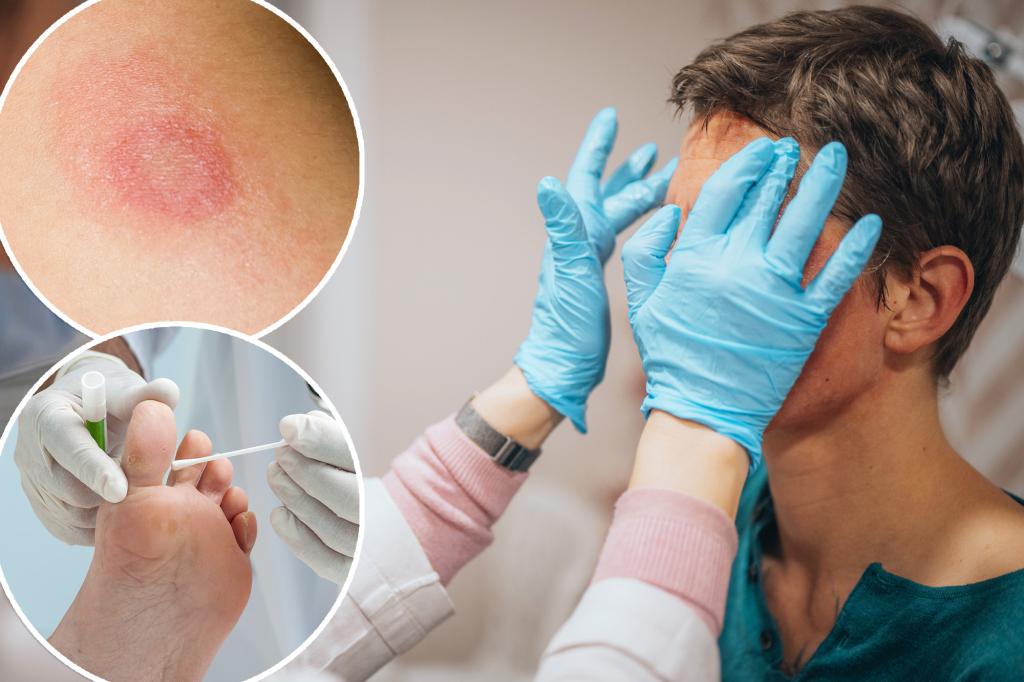
Health experts are warning of new and highly contagious strains of fungus after a NYC man in his 30s developed a sexually transmitted form of ringworm — the first reported case in the US.
Healthcare providers should be aware that Trichophyton mentagrophytes type VII [TMVII] is the latest in a series of serious skin infections that have now reached the United States,” said Dr. Avrom S. Caplan, an assistant professor in the department of dermatology at NYU Grossman School of Medicine.
Caplan co-authored a case study published Wednesday about an unnamed New York man who contracted TMVII, with a skin rash that appeared on his penis, buttocks and limbs.

Cases of TMVII have been increasing in Europe, especially among men who have sex with men.
The man in the new case study had visited England, Greece and California. He reported having sex with men during his travels, none of whom revealed similar skin problems.
“Since patients are often reluctant to discuss genital problems, physicians should ask directly about rashes around the groin and buttocks, especially for those who are sexually active, have recently traveled abroad, and report areas of itching elsewhere on the body,” the author old study. Dr. John G. Zampella advised.
Zampella noted that infections caused by TMVII seem to respond to standard antifungal therapies such as the drug terbinafine (also known as Lamisil), but they can take months to clear up.
They can also be mistaken for lesions caused by eczema, which can delay treatment.
A different itchy, sticky skin infection that causes a TMVII-like rash is proving to be a bigger challenge for dermatologists.

Trichophyton indotineae — which is widespread in India and was first confirmed in the U.S. last year — often resists treatment with terbinafine, NYU Grossman School of Medicine researchers said.
They analyzed data from 11 men and women treated for Trichophyton indotineae in NYC hospitals between May 2022 and May 2023.
Seven of the patients received standard doses of terbinafine.
Their rashes did not disappear, possibly due to genetic mutations in the fungus.
The antifungal pill itraconazole produced better results, but Caplan warned that the drug can interfere with other medications and cause nausea and diarrhea, among other side effects.
Caplan said that while dermatologists should be on the lookout for TMVII and Trichophyton indotineae, rates in the U.S. so far remain low.
His team hopes to expand their research on the two types of mushrooms over the next few months.
“These [initial] The findings provide new insight into how some of the fungal skin infections spreading from South Asia may evade our therapies,” Caplan said. “Beyond learning to recognize their deceptive signs, clinicians will need to ensure that their treatment to address each patient’s quality of life needs.”
#sexually #transmitted #fungal #infection #discovered #NYC #case
Image Source : nypost.com